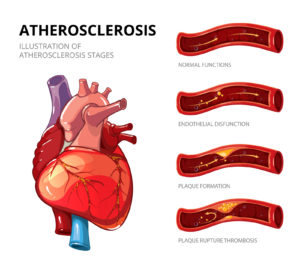
Growing scientific evidence continues to highlight the health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly for cardiovascular protection. A large observational study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association reports that individuals with higher circulating omega-3 levels have a significantly lower risk of developing atrial fibrillation (AF), one of the most common heart rhythm disorders.
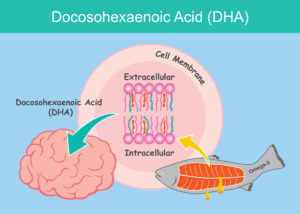
Omega-3 fatty acids—especially EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid)—are widely recognized for their heart-protective, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic health benefits. Among the most well-documented health benefits of omega-3 are support for normal heart rhythm, improved vascular function, reduced triglyceride levels, and protection against chronic inflammation.
Key Findings From the Study
Researchers analyzed data from the UK Biobank and observed that:
- Participants with the highest blood levels of omega-3 fatty acids experienced the lowest incidence of atrial fibrillation.
- The association between omega-3 status and heart rhythm health was strongest when omega-3 levels were measured directly in the bloodstream.
- Self-reported fish oil supplement use alone did not reliably predict atrial fibrillation risk, emphasizing that the health benefits of omega-3 depend on achieving adequate blood levels, not just occasional supplementation.
These findings reinforce the importance of maintaining optimal omega-3 status to fully realize the health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly for heart rhythm stability and cardiovascular risk reduction.
Why the Health Benefits of Omega-3 Extend Beyond Heart Rhythm
In addition to supporting normal cardiac electrical activity, the health benefits of omega-3 extend to many other systems in the body. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for:
- Cardiovascular health, including improved endothelial function and reduced arterial inflammation
- Brain and cognitive health, supporting memory, mood, and neurological function
- Eye health, as DHA is a major structural component of the retina
- Joint and muscle health, by modulating inflammatory pathways
- Metabolic health, including insulin sensitivity and lipid balance
Because omega-3 fatty acids influence inflammation and cell membrane function throughout the body, their benefits are systemic and long-lasting when adequate levels are maintained.
What This Research Means for Long-Term Health
This study adds to the expanding body of research showing that the health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids go beyond cholesterol management, playing a meaningful role in protecting against atrial fibrillation and other cardiovascular conditions. Maintaining optimal omega-3 levels through diet and high-quality supplementation may be an important strategy for promoting heart health, reducing stroke risk, and supporting overall longevity. Here is link to the actual study .
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/JAHA.125.043031